Ecological pyramids
Graphic representation of the trophic structure and function at successive trophic levels of an ecosystem is called ecological pyramids. The concept of ecological pyramids was introduced by Charles Elton (1927). Thus they are also called as Eltonian pyramids.
There are three types:
(1) pyramid of number
(2) pyramid of biomass
(3) pyramid of energy
.1. Pyramid of number
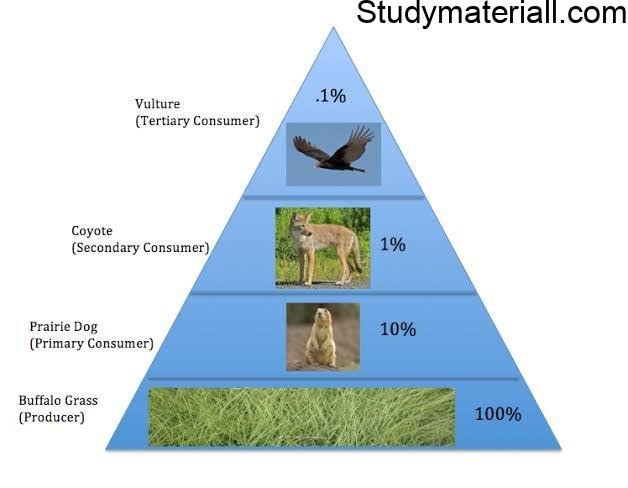
A graphical representation of the number of organisms present at each successive trophic level in an ecosystem is called pyramids of number. There are three different shapes of pyramids upright, spindle and inverted. There is a gradual decrease in the number of organisms in each trophic level from producers to primary consumers and then to secondary consumers, and finally to tertiary consumers. Therefore, pyramids of number in grassland and pond ecosystem are always upright.In a forest ecosystem the pyramid of number is somewhat different in shape, it is because the base (T1) of the pyramid occupies large sized trees (Producer) which are lesser in number. Herbivores (T2) (Fruit eating birds, elephant, deer) occupying second trophic level, are more in number than the producers. In final trophic level (T4), tertiary consumers (lion) are lesser in number than the secondary consumer (T3) (fox and snake). Therefore, the pyramid of number in forest ecosystem looks spindle shaped.The pyramid of number in a parasite ecosystem is always inverted, because it starts with a single tree. Therefore there is gradual increase in the number of organisms in successive tropic levels from producer to tertiary consumers.
2 Pyramid of biomass

A graphical representation of the amount of organic material (biomass) present at each successive trophic level in an ecosystem is called pyramid of biomass.In grassland and forest ecosystems, there is a gradual decrease in biomass of organisms at successive trophic levels from producers to top carnivores (Tertiary consumer). Therefore, these two ecosystems show pyramids as upright pyramids of biomass.However, in pond ecosystem, the bottom of the pyramid is occupied by the producers, which comprise very small organisms possessing the least biomass and so, the value gradually increases towards the tip of the pyramid. Therefore, the pyramid of biomass is always inverted in shape.
3. Pyramid of energy
A graphical representation of energy flow at each successive trophic level in an ecosystem is called pyramid of energy. The bottom of the pyramid of energy is occupied by the producers. There is a gradual decrease in energy transfer at successive tropic levels from producers to the upper levels. Therefore, the pyramid of energy is always upright.




